Core Web Vitals explained with GIFs
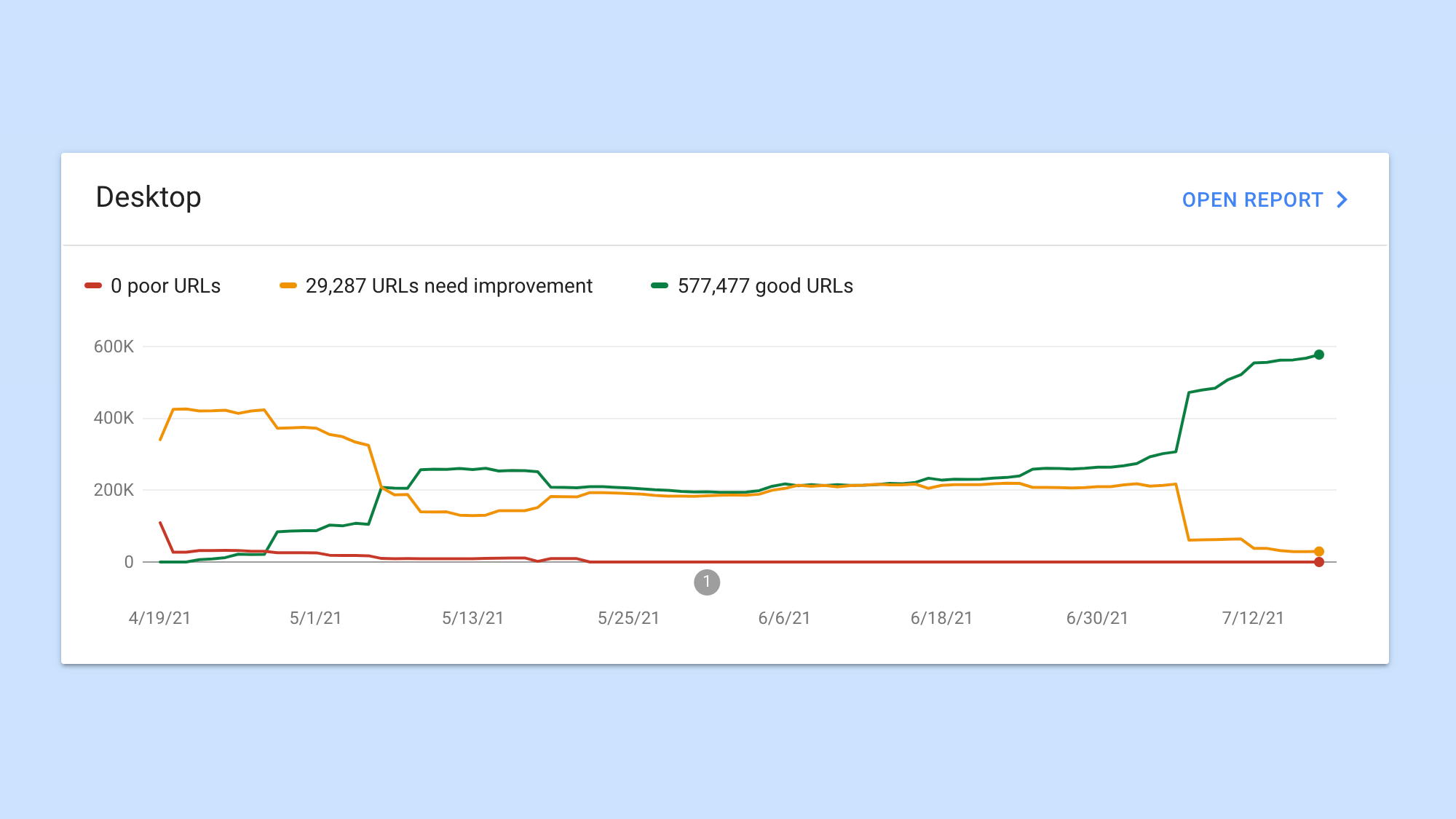
Passing your Core Web Vitals and google will reward you with visibility.
With Google’s June 2021 update Core Web Vitals (CWV) will become a factor in SEO ranking. It measures the quality of a site by these three metrics: LCP, FID and CLS.
If you pass all of them them, Google will reward you with more visibility.
You can check how well you do on these metrics via several ways:
- Pagespeed Insights
- Search Console
- WebDev Measure
- Chrome DevTools & Lighthouse
- Web Vitals Chrome Extension
- Custom event tracking with Google Analytics
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP marks the point in the page load timeline when the page’s main content has likely loaded.
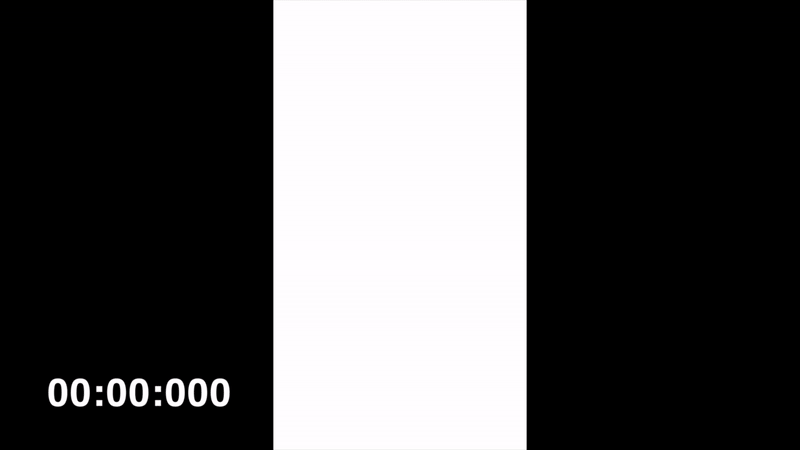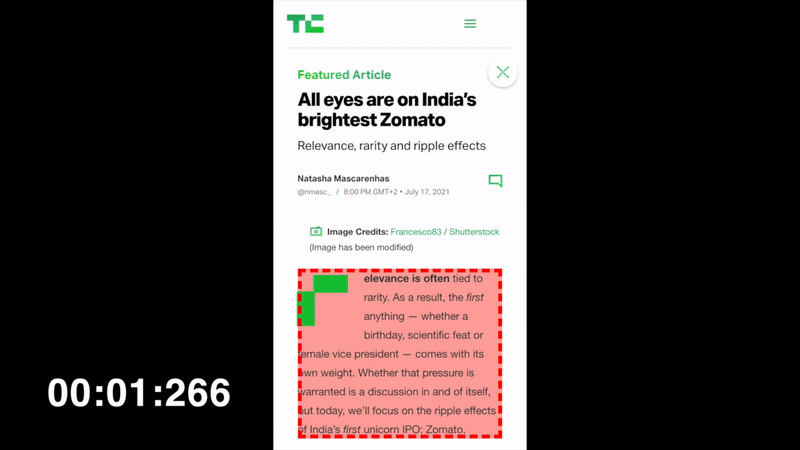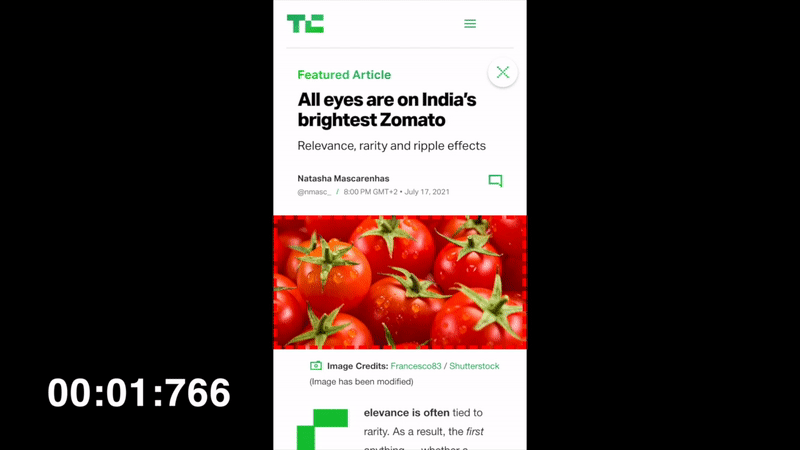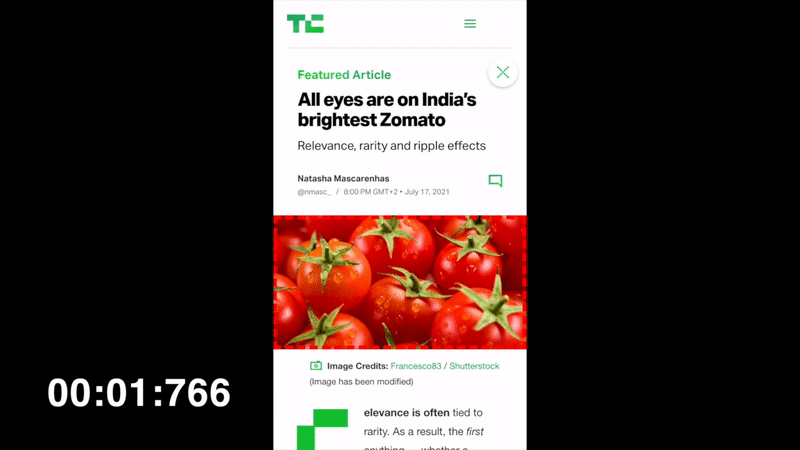
LCP will keep changing until the Largest Contentful Paint is done, which here is at 1.766s
The faster you make the biggest content on the above-the-fold appear, the better your metric will be.
If you can preload the biggest image already, e.g. with <link rel="preload" href="..."> or make the content appear without rendering it with your Javascript Framework, you’ll win big.
Causes of LCP:
- Slow server response times
- Render-blocking Javascript and CSS
- Slow resource load times
- Client-side rendering
First Input Delay (FID)
FID measures the time from when a user first interacts with a page to the time when the browser is actually able to begin processing event handlers in response to that interaction.

0.666s pass until you see the website working with your interaction.
Javascript is synchronous and single-threaded. If a user interaction happens while the thread is busy, the user has to wait. If you have too many libraries that load at runtime, worse even if you don’t need them right away, this can increase the FID.
It’s similar to TTI (Time to Interactive) that you might have heard of already. However FID will only start to be measured from the user interaction. Whereas TTI will be measured from the very start of loading the site.
Causes of FID:
- too much javascript code to execute right away, especially 3rd party
- ad networks can push lots of unneeded Javascript
- not using code-splitting (e.g. with webpack, Rollup, Parcel)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS is a measure of the largest burst of layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifespan of a page.

CLS is happening here that makes the content jump around.
Layout shifts only happen when an element higher up is making other elements move. If the element is changing and there is nothing after it, it doesn’t count as a layout shift—as well as DOM changes that were caused by a user interaction with a grace period (500ms).
Note: Mobile viewports and 3G devices will cause much more CLS. Make sure to throttle your connection while optimising your page for these metrics.
Causes of CLS:
- images without size attributes
- requests finish later that will inject content above existing content
- lazy loaded components
If you found this post interesting please leave a ❤️ on this tweet and consider following my 🎢 journey about #webperf, #buildinpublic and #frontend matters on Twitter.
CORE WEB VITALS 📈
— Simon Wicki (@zwacky) July 21, 2021
With Google's June 2021 update CWV becomes a factor in SEO ranking. It measures the quality of a site by these three metrics: LCP, FID and CLS.
If you pass them, Google will reward you with more visibility.
Read on what they are and how to measure them. 👇 pic.twitter.com/KSng9XaX1O

Simon Wicki is a Freelance Developer in Berlin. Worked on Web and Mobile apps at JustWatch. Fluent in Vue, Angular, React and Ionic. Passionate about Frontend, tech, web perf & non-fiction books.